Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are two groups of fats our bodies cannot make. They must be consumed in our diet.
Omega-3s are generally considered to be anti-inflammatory in nature. On the other hand, Omega-6s are pro-inflammatory. Although both are important for our health, our ancestors would have typically consumed these fatty acids in equal amounts. However, a diet too high in omega-6 fatty acids can increase inflammation, bringing a higher risk of many chronic diseases.
A healthy ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids appears to be between 1:1 to 1:4. However, studies suggest that people who follow a typical Western diet may consume 2—25 times more omega-6 due to the high consumption of fast and processed foods, hydrogenated fats like corn oil and other vegetable oils. This imbalanced ratio can cause systemic inflammation throughout the body and lead to chronic disease.
There are three main forms of omega-3 fats: DHA, EPA and ALA. Whilst all are important for our health, particular benefits have been found in EPA and DHA.
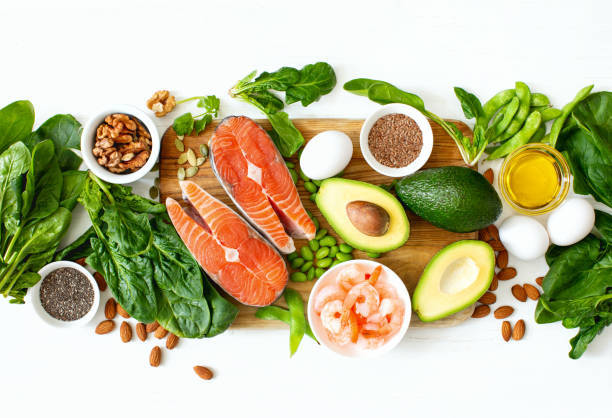
Top Omega-3 foods are: fish (aim for small and wild fish that contain less heavy metals), algae, seafood, flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds and walnuts.

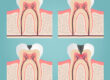
Omega-3s help reduce inflammation in the body and therefore play an important role in the prevention and management of a number of diseases including periodontal disease.
Some research has shown an association between omega-3 fats and gum health; even dietary supplementation with modest levels of fish oil (that is rich in omega-3) could potentially be a cost-effective adjunctive therapy to manage periodontal disease.