Today we will continue where we left off on the last blog post, and we will explain how the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 is an important biomarker of inflammation.
Inflammation refers to the body’s process of fighting off infections, injuries, and toxins, in an attempt to heal itself. When something damages our cells, our body releases chemicals that trigger a response from our immune system.
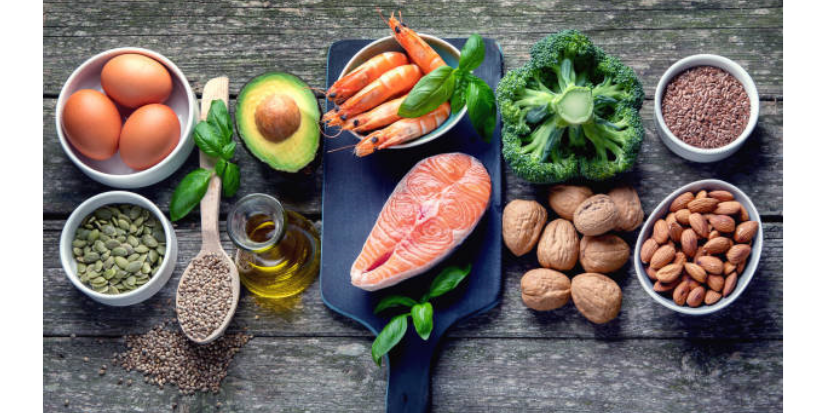
Notably, omega-3 fatty acids can reduce the production of molecules and substances linked to inflammation, such as inflammatory eicosanoids and cytokines. Studies have consistently observed a connection between higher omega-3 intake and reduced inflammation. Therefore, omega-3 plays an important role in the prevention and management of a number of chronic diseases.
There are nutritional tests that measure the omega 6 to omega 3 ratios and will inform if the balance is right, or if it’s necessary to do some changes in diet to improve those levels.
Measuring the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio is an important risk factor for diseases like heart disease, Alzheimer’s and other inflammatory diseases. The test can also measure amounts of specific omega-3s called EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) in the red blood cell membranes. It is reported as a percentage and has clinical meaning as an important biomarker of inflammation. Knowing the omega-3 to omega-6 ratio can help to personalize the omega-3 intake and support good health.
Refer to our last blog post for suggestions on how to increase the quantity of omega-3s in your diet. Additionally, the connection to gum health is also discussed.